A Digital Atlas of Ion Channels Expression Patterns in the Two-Week-Old Rat Brain
Volodymyr Shcherbatyy (Department of Genes and Behavior, Max Plank Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen), James Carson (Biological Sciences Division, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA), Murat Yaylaoglu (Department of Genes and Behavior, Max Plank Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen), Katharina Jaeckle (Department of Genes and Behavior, Max Plank Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen), Frauke Grabbe (Department of Genes and Behavior, Max Plank Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen), Maren Brockmeyer (Department of Genes and Behavior, Max Plank Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen), Ezekiel Gomez (Biological Sciences Division, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA), Tao Ju (Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO), Gregor Eichele (Department of Genes and Behavior, Max Plank Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen)
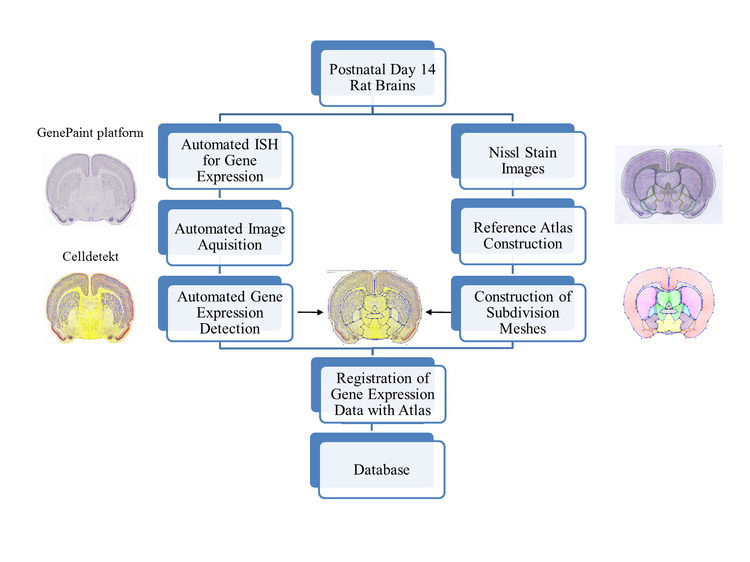
The Allen Brain Atlas [1] provides a first important step towards the goal of standardization. It contains the expression patterns of ~300 ion channels in serial sections through the adult mouse brain. We have developed highly reproducible methods of brain orientation so that data obtained from different specimens can be used for comparative analysis. Moreover, we have re-determined the expression patterns of nearly all ion channels in the two-week-old rat brain, a specimen frequently used for electrophysiological studies. Furthermore, we used a previously developed atlasing method (subdivision meshes) to faithfully model the shape of the various brain regions [2] and quantified gene expression strength [3], following a previously established procedure (http://www.geneatlas.org).
We illustrate our approach using inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir) and show some of the quantitative comparisons of the expression patterns and strengths to emphasize the usefulness of this new digital atlas.
References:
1. Lein, E.S., et al., Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature, 2007. 445(7124): p. 168-76.
2. Carson, J.P., et al., A digital atlas to characterize the mouse brain transcriptome. PLoS Comput Biol, 2005. 1(4): p. e41.
3. Carson, J.P., G. Eichele, and W. Chiu, A method for automated detection of gene expression required for the establishment of a digital transcriptome-wide gene expression atlas. J Microsc, 2005. 217(Pt 3): p. 275-81.

 Latest news for Neuroinformatics 2011
Latest news for Neuroinformatics 2011 Follow INCF on Twitter
Follow INCF on Twitter