Automated Functional MRI Quality Assessment
Filed under:
Neuroimaging
Gabriele Fariello (Harvard University / Massachusetts General Hospital), Victor Petrov (Massachusetts General Hospital), Timothy O'Keefe (Harvard University), Garth Coombs (Massachusetts General Hospital)
Gabriele R. Fariello (1,2,3), Victor I. Petrov (1,3), Timothy M. O’Keefe (1,2), Garth Coombs (3), and Randy L. Buckner (1,2,3,4)
1. Harvard University, Neuroinformatics Research Group
2. Harvard University, Center for Brain Science
3. Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital
4. Howard Hughes Medical Institute
The ability to quickly assess the quality of acquired functional imaging data within large data sets in an automated, reliable, and meaningful manner is of increasing importance. Automated quality assurance metrics are of particular value when managing multi-center imaging studies and also when studying patient populations where movement and degraded data quality can confound results (e.g., Van Dijk et al., 2012; Powers et a., 2012). With the release of large publicly accessible fMRI data sets such as the 1000 Functional Connectomes Project (Biswal et al., 2010), the future release of the NIH Human Connectome Project data (Van Essen et al., 2012), and the Brain Genomics Superstruct Project Open Data Set, having quantitative quality control metrics will be essential.
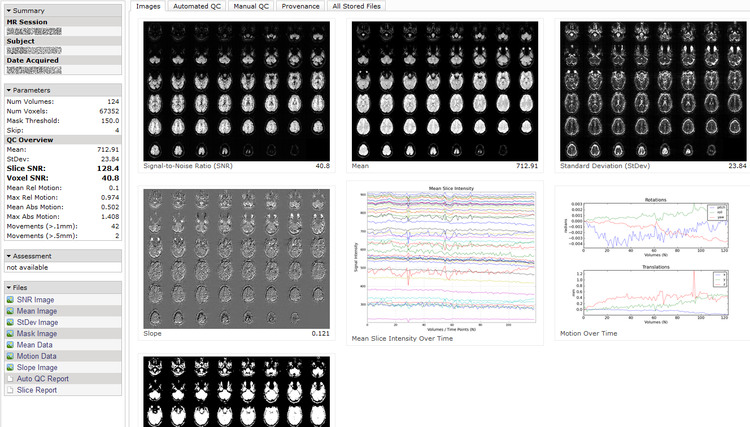
Here we present an effective automated quality assessment method for BOLD fMRI images. It includes relevant metrics such as voxel and slice-intensity based SNR calculations, movement metrics, mean, standard deviation, SNR and slope images, as well as motion and mean-slice intensity plots in a convenient, one-page display format. The full display can be used for in depth vetting and four summary statistics can be used when extracted values are needed.
Source code used to generate output images, reports, and values will be made available from a bitbucket repository.
1. Harvard University, Neuroinformatics Research Group
2. Harvard University, Center for Brain Science
3. Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital
4. Howard Hughes Medical Institute
The ability to quickly assess the quality of acquired functional imaging data within large data sets in an automated, reliable, and meaningful manner is of increasing importance. Automated quality assurance metrics are of particular value when managing multi-center imaging studies and also when studying patient populations where movement and degraded data quality can confound results (e.g., Van Dijk et al., 2012; Powers et a., 2012). With the release of large publicly accessible fMRI data sets such as the 1000 Functional Connectomes Project (Biswal et al., 2010), the future release of the NIH Human Connectome Project data (Van Essen et al., 2012), and the Brain Genomics Superstruct Project Open Data Set, having quantitative quality control metrics will be essential.
Here we present an effective automated quality assessment method for BOLD fMRI images. It includes relevant metrics such as voxel and slice-intensity based SNR calculations, movement metrics, mean, standard deviation, SNR and slope images, as well as motion and mean-slice intensity plots in a convenient, one-page display format. The full display can be used for in depth vetting and four summary statistics can be used when extracted values are needed.
Source code used to generate output images, reports, and values will be made available from a bitbucket repository.
Preferred presentation format:
Poster
Topic:
Neuroimaging

 Latest news for Neuroinformatics 2011
Latest news for Neuroinformatics 2011 Follow INCF on Twitter
Follow INCF on Twitter